Parotid & Submandibular Gland Injury Treatment
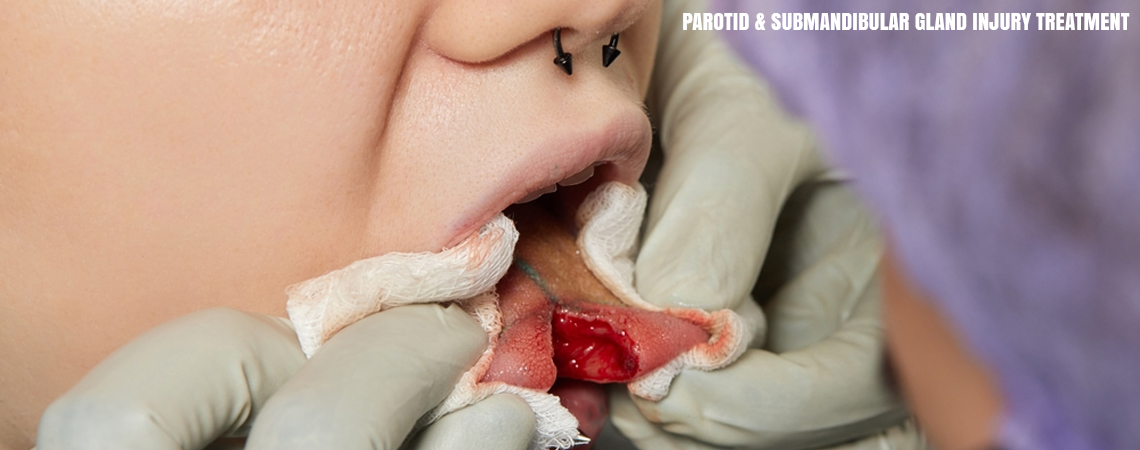
The parotid and submandibular glands are major salivary glands responsible for saliva production, which aids digestion and maintains oral health. Injury to these glands—whether due to trauma, surgery, infection, or tumors—can cause pain, swelling, saliva leakage, facial nerve issues, and functional discomfort.
At Paras Hospital, we provide advanced diagnostic evaluation and surgical management for parotid and submandibular gland injuries, ensuring safe restoration of function while preserving facial aesthetics and nerve integrity.
Understanding Parotid & Submandibular Gland Injuries
Parotid Gland Injury
The parotid gland is located in front of the ear and extends toward the cheek. Injuries here are complex due to the close association with the facial nerve, which controls facial movement.
Submandibular Gland Injury
The submandibular gland lies beneath the jaw. Injury can affect saliva flow, cause pain during eating, or lead to swelling and infection.
Common Causes:
- Facial trauma or road traffic accidents
- Penetrating injuries or cuts to the face and neck
- Surgical complications
- Salivary gland tumors
- Infections or abscess formation
- Salivary duct obstruction or leakage (salivary fistula)
Symptoms of Gland Injury
Patients may experience:
- Swelling near the ear, jaw, or neck
- Pain or discomfort while chewing
- Saliva leakage from wound or skin
- Dry mouth or difficulty swallowing
- Recurrent infections
- Facial weakness (in parotid gland involvement)
Early diagnosis is essential to prevent long-term complications.
Diagnosis and Evaluation
At Paras Hospital, diagnosis may include:
- Detailed clinical examination
- Ultrasound or CT/MRI scans
- Sialography (duct imaging) when required
- Facial nerve assessment (for parotid injuries)
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the severity, cause, and gland involved.
Conservative Management
- Antibiotics for infections
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Saliva-controlling measures
- Observation for minor injuries
Surgical Management
- Repair of salivary ducts
- Management of salivary fistula
- Partial or complete gland excision (when indicated)
- Facial nerve preservation and reconstruction (if affected)
- Removal of tumors or damaged tissue
Our surgical approach prioritizes functional recovery, nerve safety, and minimal scarring.
Recovery and Aftercare
- Most patients recover well with proper care
- Temporary swelling or stiffness may occur
- Diet modifications may be advised initially
- Follow-up ensures healing and saliva function restoration
Our multidisciplinary team ensures smooth recovery with personalized post-treatment care.
Why Choose Paras Hospital?
- Highly experienced reconstructive & head-neck surgeons
- Advanced surgical facilities
- Precision-focused nerve preservation techniques
- Comprehensive post-operative care
- Trusted tertiary care expertise
We focus on restoring comfort, function, and quality of life for every patient.